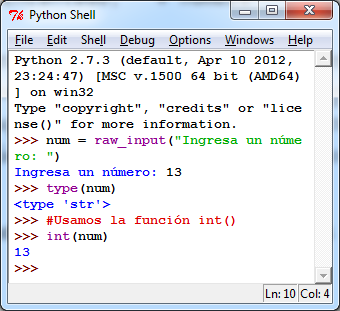
Vamos a ver un ejemplo para ver los tipos de datos que existen en C#, aprenderemos a declarar variables y constantes de tipo, también veremos los operadores más comunes a usar en C#. Las conversiones implícitas y explicitas.
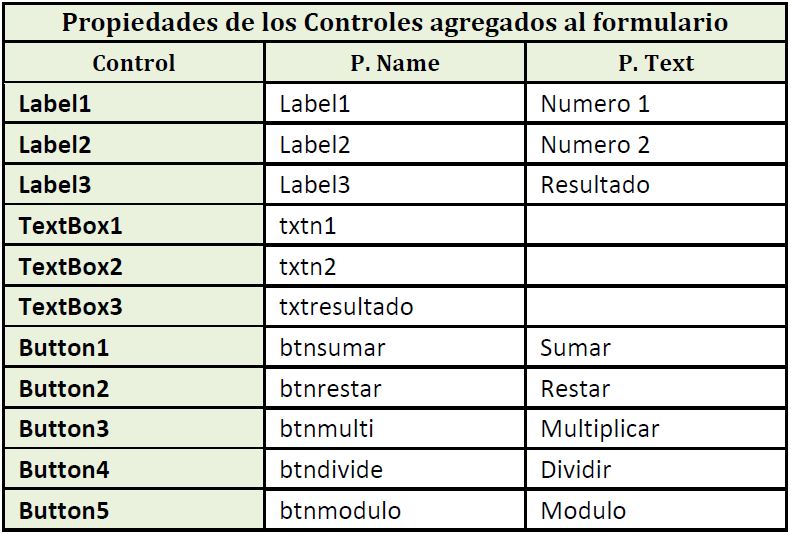
Como ejemplo desarrollamos un programa que permita sumar, restar, multiplicar, dividir y obtener el módulo de dos números y muestre el resultado. Agregar 3 Labels para las etiquetas, 3 TextBox y 5 Button.
– Debemos de hacer doble clic en el botón Sumar para poder escribir código en el.
Código para el botón SUMAR:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | // Código para el botón SUMAR private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Declaramos variables y asignamos los respectivos valores int n1 = int.Parse(txtn1.Text); // Forma para realizar la conversión a entero int n2 = int.Parse(txtn2.Text); int r = n1 + n2;// Realizamos la suma txtresultado.Text = r.ToString(); } |
Código para el botón RESTAR:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | // Código para el botón RESTAR private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Declaramos variables y asignamos los erspectivos valores int n1 = int.Parse(txtn1.Text); int n2 = int.Parse(txtn2.Text); int r = n1 - n2;//Realizamos la resta txtresultado.Text = r.ToString(); } |
Código para el botón MULTIPLICAR:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | // Código para el botón MULTIPLICAR private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { int n1 = int.Parse(txtn1.Text); int n2 = int.Parse(txtn2.Text); int r = n1 * n2;// Realizamos la multiplicación txtresultado.Text = r.ToString(); } |
Código para el botón DIVIDIR:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | // Código para el botón DIVIDIR private void button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { int n1 = int.Parse(txtn1.Text); int n2 = int.Parse(txtn2.Text); int r = n1 / n2; // Realizamos la división txtresultado.Text = r.ToString(); } |
Código para el botón MODULO:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | // Código para el botón MODULO private void button5_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { int n1 = int.Parse(txtn1.Text); int n2 = int.Parse(txtn2.Text); int r = n1 % n2;// Realizamos el módulo txtresultado.Text = r.ToString(); } |
A continuación les muestro todo el código completo :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 | using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace Leccion2_1Form // Tipos de variables y Operadores { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Declaramos variables y asignamos los respectivos valores int n1 = int.Parse(txtn1.Text); int n2 = int.Parse(txtn2.Text); int r = n1 + n2;// Realizamos la suma txtresultado.Text = r.ToString(); } private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Declaramos variables y asignamos los erspectivos valores int n1 = int.Parse(txtn1.Text); int n2 = int.Parse(txtn2.Text); int r = n1 - n2;//Realizamos la resta txtresultado.Text = r.ToString(); } private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { int n1 = int.Parse(txtn1.Text); int n2 = int.Parse(txtn2.Text); int r = n1 * n2;// Realizamos la multiplicación txtresultado.Text = r.ToString(); } private void button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { int n1 = int.Parse(txtn1.Text); int n2 = int.Parse(txtn2.Text); int r = n1 / n2; // Realizamos la división txtresultado.Text = r.ToString(); } private void button5_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { int n1 = int.Parse(txtn1.Text); int n2 = int.Parse(txtn2.Text); int r = n1 % n2;// Realizamos el módulo txtresultado.Text = r.ToString(); } } } |
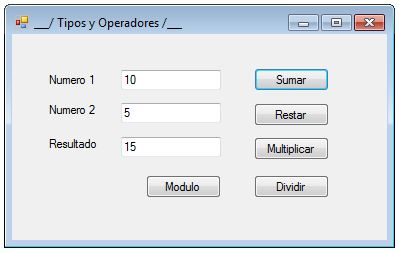
Resultado: